
Many compliance standards focus on protecting individual personal information and sensitive data in a world rife with cyber-attacks and data breaches. Now, companies need to make their systems immune to digital intrusion and prepared to reduce the attack surface for strong information security measures around private information.
Data breaches are becoming a norm through the rapid transition of physical businesses to online businesses and more online activities. Each day we come across the news of cyber attacks resulting in sensitive data breaches and sensitive information posted on the DarkWeb portals or hackers’ forums.
This blog post covers the basics of a data breach, along with the impact and the most famous examples. But before we dive into data breaches happening in today’s world, we must know what data breaches are and how many different types there are. Some of the reasoning in this topic stems from our experiences during risk findings from penetration testing and other security assessments.
What is a data security breach?
A data security breach involves unauthorised access to, disclosure of, or loss of Personal Data transmitted, stored or otherwise processed. It includes unlawful or unauthorised access to personal information kept on a server/in storage; the accidental or unlawful destruction, alteration, identity theft (such as full names, national insurance numbers, social security numbers, PII), disclosure of, or loss of records containing personal information or financial information.
A data breach is when a person or entity gains access to someone else’s data without permission. That data could be anything from personal information like credit card numbers and social security numbers to bank account passwords, photographs of your family, company trade secrets, etc. And the consequences can be devastating. Multiple studies and researches have analysed leaked data that amounts to billions of records stolen via data breaches, and this number has been rising steadily. The cost of these breaches can range anywhere from $100 for an individual’s payment card number to millions for a mega-breach at a large corporation with multi-million customers and employees.
What is considered a data security breach?
By definition, a data breach is described as a security incident that leads to unauthorised access to personal data or release of confidential, sensitive or personal information, which is not meant for public disclosure.
A data breach includes the intentional, unintentional, accidental, unlawful destruction, loss, alteration or compromisation of stored or processed information. It can result in the release of business secrets, Personally Identifiable Information (PII), Personal Health Information (PHI), debit or credit card information or any other personal data discharge or identity theft. It usually occurs for ransomware or arises due to espionage activity. Data protection is an important element of their business strategy for healthcare and social care.
Data breaches are generally defined into three categories, and depending on the affected principles of information security, they might involve any or all of the three categories.
Breach of confidentiality: This data breach appears when there is unauthorised or untrusted access or disclosure to people’s info or businesses’ proprietary information.
Breach of availability occurs when destruction or accidental breakage befalls either to destroy personal data or business-sensitive information or prevent legitimate access to data.
Breach of integrity: It happens due to an unauthorised or accidental alteration of personal data. Learn detailed data integrity concepts here.
What if stolen data is encrypted?
It still matters if your encrypted data is stolen. There are examples of encryption flaws where unsalted hashes are stolen that can be matched with fast computing resources. For instance, the SHA1 hash of the string’ theworstpassword’ will always remain 82098597C501E751188DAE85366BAAB92257F40E. However, if a salt is added to the clear text password and then a hash is generated. The value will be different, and to reverse it to clear-text would require the knowledge of salt value.
Attackers perform this attack by generating many hashes from a list of known passwords and decrypting passwords easily. Read more about encryption and hashing here.
Data breaches life cycle.
The process of first detecting personal data breach to completing the cleanup. Every cycle will have a different phase according to the stage of the cycle. The data breach life cycle involves significant areas such as “data breach response” or “data breach aftermath”. Typically targeted data breach methodology by attackers consists of research, attack vector, exploitation and exfiltration. Should you wish to read in-depth details, read our article about the cyber kill chain.
What are the different types of data breaches?
Cybercriminals are getting more sophisticated with each passing day; they bring out new tactics and customised techniques to bypass security controls. You must be aware of multiple types of data breaches to implement necessary and strict controls to make your assets resilient against security incidents and reduce the chances of a personal data breach. The following list is not a comprehensive list of attack vectors or attack types amounting to data breaches.
Physical breach
This type of data breach is the most common among other breaches where you lose control over your sensitive data directly. We as humans are capable of making mistakes, and in such situations, breaches occur that influence business and the individual self.
It can happen as a result of:
- An employee sending the information to the wrong recipient or misplacing the classified/sensitive information.
- An insider threat actor sending the trade secrets to the competitors
- Any robbery happens inside the organisation’s premises
- Any employee or yourself leaving the confidential file open on the desk or any public place.
- Any employee or friend stealing the information and later selling outside or using otherwise for personal gains.

Phishing attack
Cybercriminals crave unauthorised access and personal data to threaten businesses and individuals for ransomware. To do so, they most of the time launch phishing attacks to trick the employees and users into clicking over a forged link or downloading malicious attachments.
Alongside the links and attachment, they often pretend to be someone credible and legitimate and ask you to give out information or credentials.
Once you click or download the received resources or give out information, the execution of malware bypasses the security controls and provide access to the system and network, which obviously helps access personal data and sensitive information stored on the system. Read how you should spot and report phishing emails.
Man in the Middle Attack (MITM)
With a man in the middle attack technique, hackers get unauthorised access to the data transmitted between a client and the server, resulting in a compromise of information confidentiality, in other words, a data breach situation. In it, the attacker intercepted communication using techniques to inject him in between the communication process.
During the interception, the attacker breaches the information confidentiality by behaving as a listener or passively stealing the personal data or might breach the data integrity by altering the data in between the transmission of data and in some cases, the attacker also impersonates the person on receiving or sending to steal or capture the information.
Password breaches
Data breaches resulting from lost or stolen and guessed passwords are pretty old and still in trend. With so many violations already in the past, a broad audience still relies upon weak passwords such as John12345!, Alice1998, 12345678, password123, etc. In contrast, the lack of a password management system in an organisation is also a big concern.
Finding a password is now relatively easy with many different techniques ranging from credential stuffing attacks to password cracking tools and breached password databases. Once the attacker gets his hands down to the correct password, either by social engineering or password attacks, he would then have a downhill journey to log in the system or files to steal, alter or destroy the data.
SQL injection and web application risks
With the data breach types mentioned above, SQL injection is also a concerning one. In SQL injection, the attacker manipulates a web application’s back-end database via a malicious SQL statement to access the database information. Depending on the attacker’s goal and access, the attacker can temper the database content or destroy the system or move laterally to access other information available on the server, system or network.
SQL Injection is only one example of a web application security risk. Read the OWASP top 10 most common API risks and web application security risks.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Another data breach occurs due to cross-site scripting web security vulnerability, which allows an attacker to execute malicious code inside the victim’s browser in the active web session. Through a successful cross-site scripting attack, the attacker can impersonate as a victim and carry out actions on his behalf. The action varies from gaining access to a user’s data or privilege account access within the web application or control over the app’s full functionality and data.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that cybercriminals often use to demand ransom by encrypting the data and blocking access to the files or system on the victim system until the ransom is paid. Ransomware is used to hold data’ hostage’ in an attempt to extract payment from victims. This attack can be made in various ways, including the use of email attachments infected with malware, direct exploitation of system vulnerabilities or visiting poisoned websites where a drive-by download infects your computer with ransomware.
Third-party vendor breaches
Third-party vendor data breaches have become more commonplace over the past few years. Earlier this year, Experian, one of the three largest bureaus used by lenders to check applicants for credit, began notifying approximately 15 million people that their personal information may have been accessed in a hack attack. It is important than ever to ensure supply chains are secure.
Breaches like these are becoming increasingly common, and many third-party vendors don’t even notify you when they happen! It’s essential to work with your security team to make sure you’re keeping up with best practices. An obvious question is: What happens if I’m using a major vendor who has breached?
What happens when there is a data breach?
A data breach can have a high magnitude impact on businesses or individuals. Whether the violation is low in severity or high, both can cause irreparable and long-lasting damage. The aftereffects can be reputational damage, loss of customers’ records and clients’ trust to hefty fines.
Data breach response is the most critical step to contain the exposure and ensure those who need to know are aware.
- Ensure that breach has been contained or stopped
- Determine the extent of data exposure. This typically includes an audit of the data accessed, timelines with many comparisons against backup data, audit logs, analysis usually performed by third-party security companies.
- You have a duty to inform those who were affected by this data breach. Not all data breaches need to be reported. GDPR Article 33 relates to the notification of a personal data breach to the authorities. The important aspect of GDPR data breach reporting time as per ICO is that it must be done within 72 hours of the breach. Those first 72 hours are critical. GDPR requires all agencies and companies to report to the appropriate authorising authority without undue delay, and this must be done within 72 hours. Further information around the eight principles of the Data Protection Act 2018 & GDPR is available here. ICO requires particular information during the time of breach notification. More information is available on how to report breaches here that discusses the following topics:
- What is a breach of data protection?
- How long to report a data breach?
- What information needs to be reported?
- What happens after reporting?
- What are the consequences of failing to report a data breach adequately?
- Can I be sacked for breaching data protection?
- What to do if my personal data is breached?
- Can you get compensation for a breach of data protection?
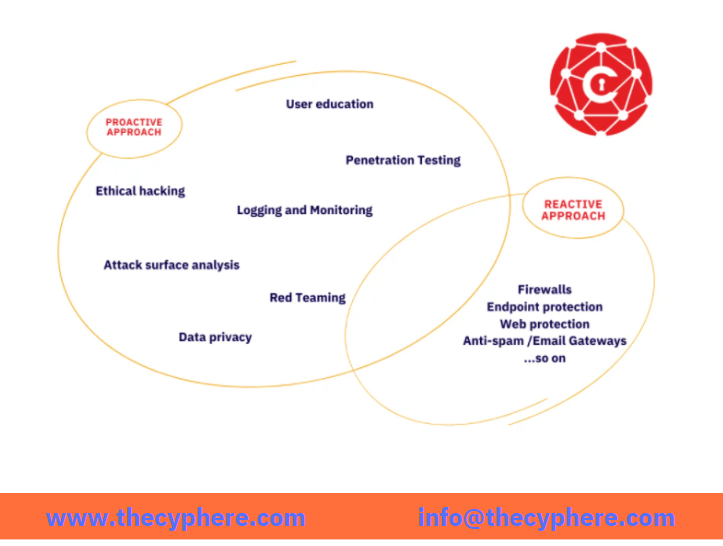
- Implement and follow the proactive security approach required at the process, people and technology level to prevent future possibilities. This should include the entire ecosystem across vendors, customers, third parties, etc., so that vulnerabilities are identified on an ongoing basis; the risk is assessed and treated by the risk management programme.
What personal data needs to be protected to prevent GDPR fines?
As per the UK-GDPR and EU GDPR, personal and sensitive personal information must be protected at any cost. This privacy law is the reason data protection has gained momentum in recent years. The data controller (the one who collects the data and defines the data processing) is liable to the legislation when the data gets exposed in any type of data breach.
If you reckon GDPR keeps cropping up in your reads every now and then, its best to give it a few minutes of your time – read here our most extensive GDPR questions and answers for employees.
GDPR defines the following item as personal data.
- Identifier’s Name
- Identification Number
- Location data
- Contact information such as a home address, email address
- IP address
- Advertising ID
The sensitive data are:
- Biometric Data
- Health data
- Genetic data
- Individual data
- Financial data
- Classified data
- Business or work information
What are examples of security breaches?
Data security breach examples in 2022 so far
Crypto.com
It’s one of the biggest businesses in its niche, crypto.com suffered a breach at the start of 2022. This attack led to funds being taken from 400+ crypto wallets.
Microsoft
As part of the Lapsus$ saga, microsoft was targeted in a limit attack attempt that was contained early. Data related to Microsoft products such as bing, cortana and other products was posted online, as seen on screenshots posted on telegram by attackers. One account was compromised in this attack. No customer data was stolen, as per Microsoft.
News Corp
News Corp, one of the biggest media houses, admitted security breach in Feb 2022 that an attack took place way back in Feb 2020. As per the business, no customer data was stolen though some emails were stolen from journalists working for nes Corp.
Ronin, FlexBooker, GiveSendGo, Cash App are some of the other names.
The top causes related to the data security breaches remain phishing and ransomware.
Data security breach examples in 2021
#1 MeetMindful data breach
MeetiMindful is a dating platform that was infiltrated by hackers and resulted in a data breach in 2021.
Affected mass:2.28 million users
Cause: Hackers exploited system vulnerability, accessed the older version of the basic user information list and later released them over the DarkWeb portal.
Breached Data:
The attack exposed a large number of personal private information such as:
- IP address
- Real names
- Email address
- City, state, and ZIP details
- Facebook user IDs
- Facebook authentication tokens
- Dating preferences
- Marital status
- Birth dates
- Bcrypt-hashed account passwords
#2 Socialarks data breach
SocialArks is a Chinese cross-border social media data-management company that offers various services for brand building, marketing, social customer management in China’s foreign trade sector.
Affected mass: 200 million records
Cause: It suffered a breach in January 2021 due to an insecure database (ElasticSearch) and an unencrypted and passwordless server leading to the lapse of data protection measures.
Breached Data: The breach includes information of social media platform users, including celebrities and influencers. The data were:
- Names
- Phone numbers
- Email addresses
- Profile descriptions
- Follower and engagement
- Locations
- LinkedIn profile links
- Connected social media accounts login names
#3 Bonobos data breach
Bonobos is a Men’s clothing store that suffered a data breach in early 2021.
Affected mass: 12.3 million records
Cause: The breach occurred when the cybercriminals compromised its backup server and dumped the stolen information on the Hacker forum.
Breached Data: Hackers were able to access the following of the Bonobos data
- 7 million shipping address records
- 1.8 million accounts information records
- 3.5 million partial credit card records.
#4 Pixlr data breach
Pixlr is a free-of-cost web-based picture-editing application among the topmost data breaches in the 2021 list.
Affected mass: 1.9 million user
Cause: The breach occurred after the cybercriminal gained unauthorised access to Pixlr’s 123rf stock photo site, which Inmagine owns. The attacker later dumped the data over the DarkWeb portal.
Breached Data: Hackers were able to access the following of the data
- Usernames
- Email addresses
- Country
- Hashed passwords
#5 Air India data breach
Air India is an Indian based airline that recently suffered a massive data breach.
Affected mass: 4.5 million customer
Cause: The breach occurred due to a cyber-attack over the Air India third-party data processing service provider named SITA
Breached Data: The lost or stolen information includes
- Passengers’ names
- Credit card numbers
- Date of birth
- Contact information
- Passport information
- Ticket information
- Star Alliance and Air India frequent flyer data
#6 Scraped data of LinkedIn users
Linkedin is a professional networking platform that made the headlines in April, suffering a data breach, only to find out scraped data from multiple websites and companies.
Affected mass: 500 million user
Cause: The breach occurred when archived data of 500 million the LinkedIn profile posted on the hacker forum with 2 million records leaked as a PoC (Proof of concept).
Breached data: The leaked professional information included
- LinkedIn IDs
- Full names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Genders
- Links to LinkedIn profiles
- Links to other social media profiles
- Professional titles and other work-related data
Data breaches example in 2020
#7 MGM Resort data breach
MGM resorts is an international American global hospitality and entertainment company.
Affected Mass: 142 million customer
Cause: The breach occurred due to authorised access to one of the hotel’s cloud servers through which the attacker stole the information of the hotel’s past guests. This data containing customer records were later put for sale over the dark web portal.
Breached Data:
- Full names
- Home addresses
- Phone numbers
- Emails
- Dates of birth
#7 EasyJet
EasyJet is a multinational low-cost British airline group.
Affected Mass: 09 million
Cause: The cause of the breach was not revealed, but according to the officials, it was a sophisticated attack on the EasyJet computer system targeted at the company’s intellectual property.
Breached Data:
- Travel details
- Email Address
- Debit credit card information
How to prevent data breaches?
Following the practical and proven methods can be used to prevent data breaches.
Assets Inventory: An asset inventory provides you with a visible understanding of hardware, software and all assets that you can prioritise based on threats and vulnerability factors and the overall security posture of your business and organisation.
Lock important files and data: Wherever your data resides, make sure to lock it with a solid and complex password. It is better if you use a password manager across all your assets. For more robust security, encrypt the data with a secure key.
Regular Audit: Having regular security audits can help you comply with regulations and governance to authenticate your internet security position. Through audits, you can identify potential compliances loopholes and security gaps that might turn into significant business risks.
A technical audit dramatically helps understand the organisation’s security posture and how the organisation manages the risk and overall internet security practices in its environment according to law and security standards.
Following are a few of the main security questions that security audits, such as penetration testing, help you answer.
- Does the organisation comply with information security policies?
- Do they follow user management, privilege management, patch management, password policies and encryption policies?
- Are there data classification and data protection measures defined by the organisation?
- Do they have end-point protection in place?
- Do they log and monitor their system logs?
- How often do they back up their data?
- How do they back up their data? Has the restore procedure been tested?
- Have they documented a security incident response plan?
- Do they have a disaster recovery and business continuity plan?
Regular Security Assessments: Penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, red teaming, etc., are the security testing that significantly helps in analysing the current security controls. Unlike the audits, these assessments practically recognise the security weaknesses, misconfiguration, threats, open path, vulnerable accesses, etc., present in the physical and virtual environment of the system, network, end-point devices, infrastructure of the organisation.
Depending on the assessment types, an organisation can answer whether they can be breached or not and how they can be breached.
Staff Training: High-end security products and assessments cannot guarantee you threat immunity nor enhance the security posture if your employees are not trained enough to counter the threats coming to them. Enforce data privacy and security policies in your organisation.
Your firewall might block the malware or malicious traffic from the outside network, but what if your employees click over the wrong URL or inject the infected USB. Such a situation can only be avoided if your employees are trained and competent enough to identify phishing or social engineering scam.
Final thoughts
There have been data breaches in the past, and there will be breaches in the future. There is no one time medicine to cure data breach, but a certain dose of security assessments and controls can help you protect your business from the data breach.
Data security breaches are on the rise, and there is no way to predict when or where they will happen. Steps of a data breach life cycle include identification and notification, remediation, detection, and response. To avoid being part of this statistic, make sure you keep all your information safe by following a proactive security approach opposite just strong passwords or encryption information.
Get in touch with our experts who can be your guards helping to protect assets by identifying all of your weaknesses and help you continuously keep a tab on the security posture. This is aligned with business requirements such as compliance and functional objectives.
Shahrukh, is a passionate cyber security analyst and researcher who loves to write technical blogs on different cyber security topics. He holds a Masters degree in Information Security, an OSCP and has a strong technical skillset in offensive security.












